[ad_1]
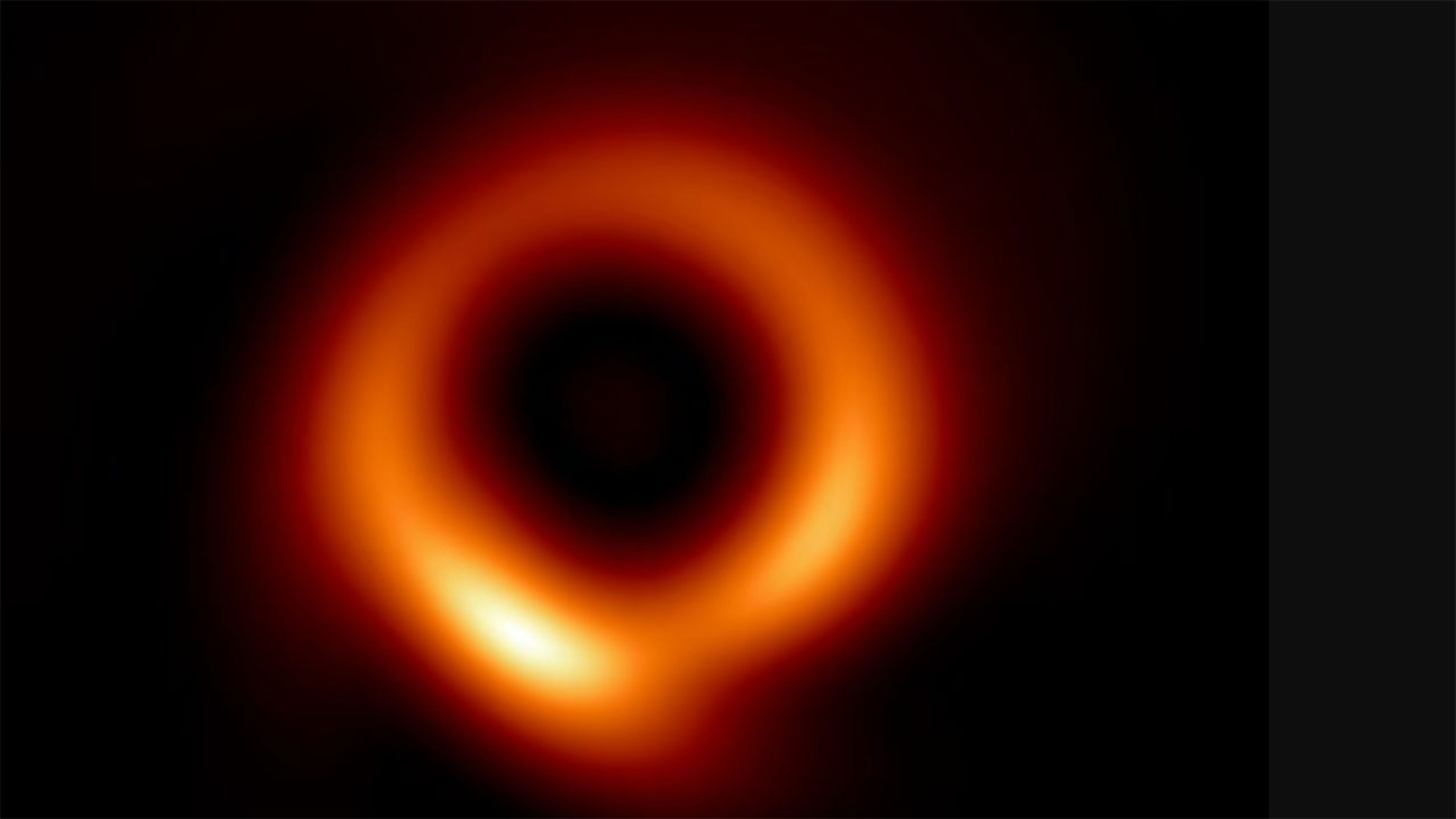
Thanks to technology, humanity now has enormous binoculars capable of looking millions of light-years away to bring us snapshots like the one we are going to share below: the first full-resolution photograph of a supermassive black hole.
This black hole It is located within the Messier 87 galaxy, 55 million light years from Earth, and yet it was the protagonist in 2019 because it was the first black hole to be directly photographed by astronomers.
But now, just four years later, and thanks to artificial intelligence, we already have a full-resolution image that reveals much more detail.
This discovery “will play a critical role in our ability to understand their behavior”, maintain the scientists, to which they add that “could help explain how this phenomenon eats matter”.

Lia Medeiros
Thanks to this image At full resolution, a central region has now been revealed that is larger and darker than first thought, and can be more clearly seen to be surrounded by glowing gas. They also found that the width of the ring in the image was much smaller than previously thought. They were able to arrive at this image with the help of data from the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT).
M87 is about 6.5 billion times the mass of our sun.
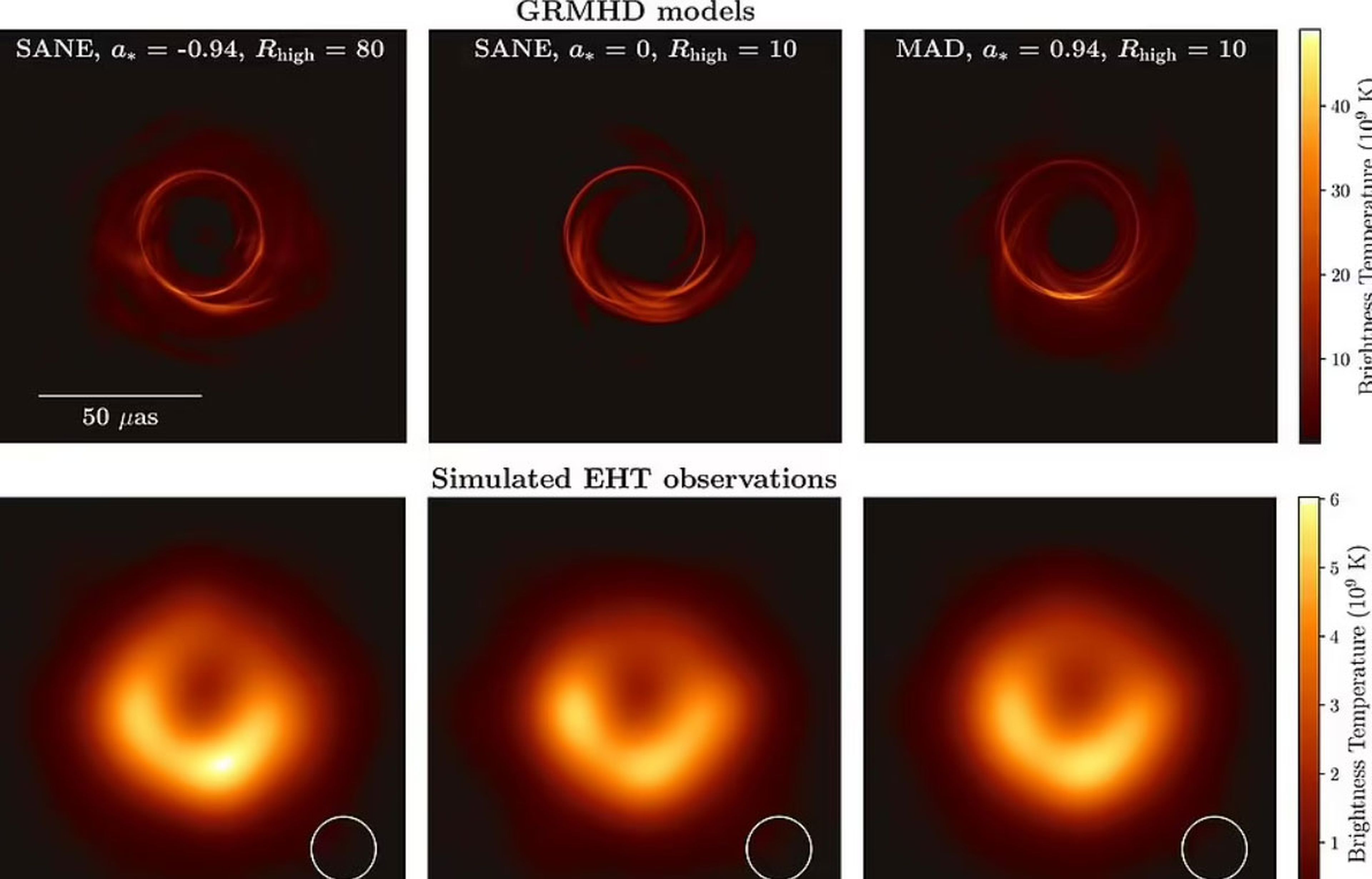
To understand this end result, remember that in 2017 the EHT used a network of seven telescopes around the world to collect data on M87. In that first image, a series of data gaps appeared like missing pieces in a puzzle, and now thanks to the artificial intelligence has been completed.
“With our new machine learning technique, PRIMO, we were able to achieve the maximum resolution of the current matrix“says the lead author, Lia Medeirosfrom the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey.

Event Horizon Telescope (EHT)
“Since we can’t study black holes up close, the detail in an image plays a critical role in our ability to understand their behavior. The width of the ring in the image is now smaller by a factor of two, which will be a powerful constraint for our theoretical models and gravity tests.“, Add.
M87 is estimated to be about 6.5 billion times the mass of our sun and spews out intense jets of energy. These jets emerge from the core of the black hole and extend at least 5,000 light-years from its center.
Artificial intelligence is based on learning under a technique that allows computers to generate rules based on large sets of training material.
This machine learning has previously been used to recreate works of art or complete some of Beethoven’s unfinished works.
“PRIMO is a new approach to the difficult task of building images from EHT observations.says Lauer.It provides a way to compensate for missing information about the object being observed, which is required to generate the image that would have been seen using a single gigantic Earth-sized radio telescope.”.
“Approximately four years after EHT released the first horizon-scale image of a black hole in 2019, we have marked another milestone, producing an image that uses the full resolution of the array for the first time. The new machine learning techniques we have developed provide a golden opportunity for our collective work to understand the physics of black holes.”, he concludes.
[ad_2]