[ad_1]
NASA’s James Webb once again surprises everyone and breaks the records of its little brother, the Hubble telescope.
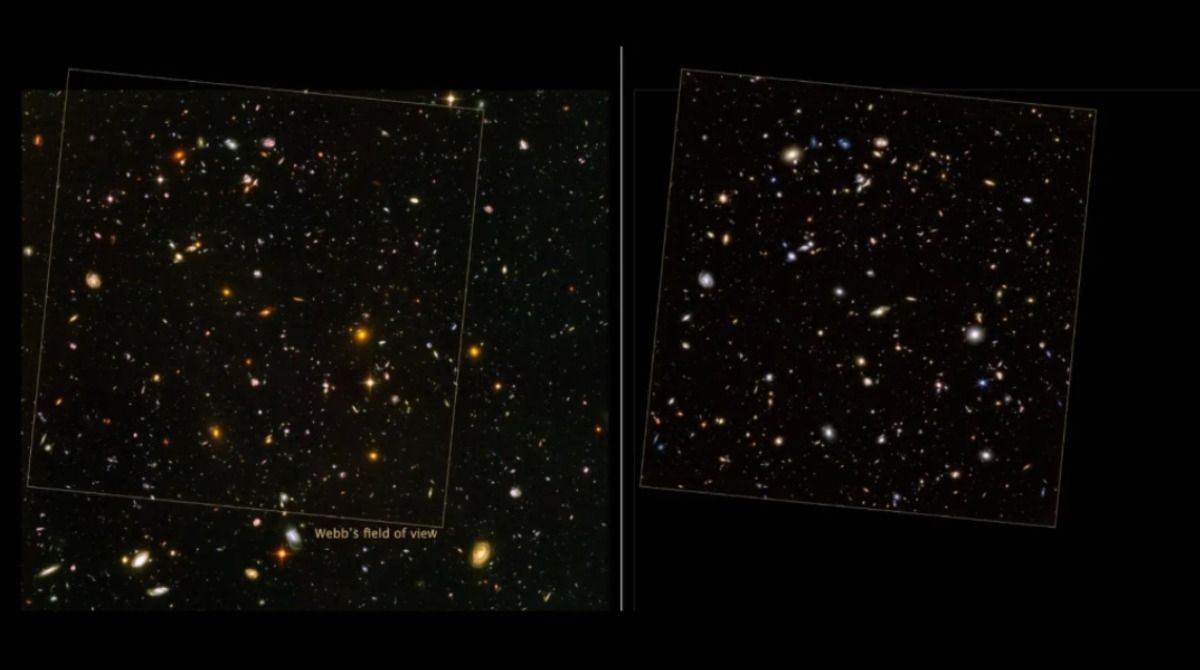
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope once again achieves a great milestone and once again shows its full potential compared to the famous Hubble telescope. In this case, the JWST has achieved the deepest view ever taken of the universe.
Until then the gold had gone to Hubble with its image called ‘Hubble Extreme Deep Field’ (Hubble eXtreme Deep Field). This was achieved by combining 10 years of photographs of the telescope -created with data from 2003 and 2004-.
Yet now the JWST in just 20 hours has managed to beat the capabilities of this incredible image managing to reveal details and possibly more distant objects that Hubble could never see.
In a few words, it was something to be expected since the latter has infrared and image sharpness capabilities far beyond the limits of Hubble —that’s what it was created for—, so it observed a deeper field than this, revealing much more data. .
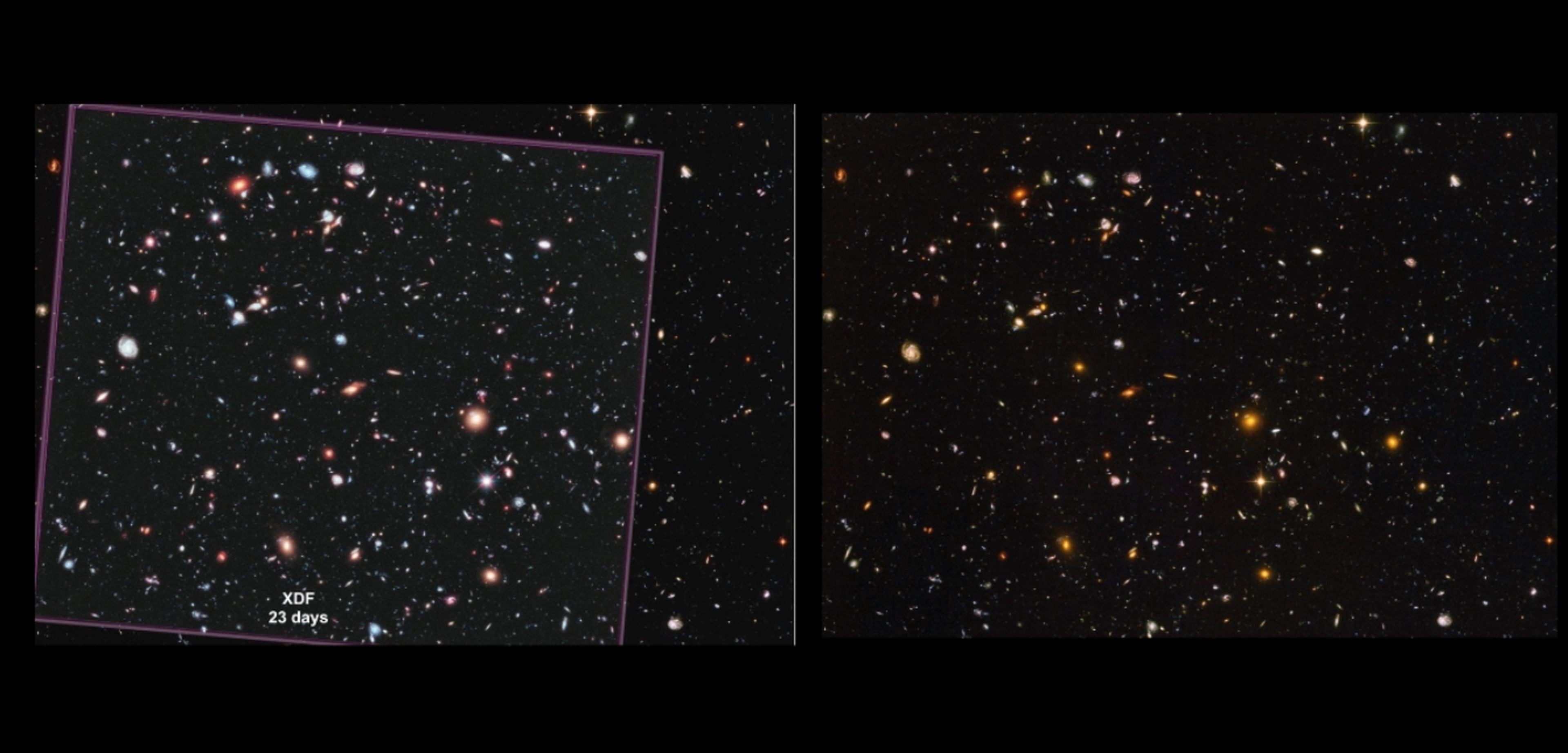

JWST once again demonstrates its full potential and improves on Hubble
Note that the resolution of the JWST images is vastly higher than that of Hubble. This resolution basically depends on the size of the mirror and the wavelength of the observed light.
Here two aspects collide, since the bigger the mirror, the more resolution, but, when it comes to the wavelength, the longer it is, the lower the resolution and it is already known that the infrared light that uses the JWST has a longer wavelength than the light observed by Hubble.
So if you both look at a wavelength of 0.7 microns at the same time, the JSWT will be able to capture some amazing images. But if the JWST observes that same object at a wavelength of 2 microns, the resolution of the resulting image will be the same as that of Hubble.
In a nutshell, JWST was designed to pick up where Hubble left off in the study of the early universe. This is why despite the high quality of Webb’s images, one cannot speak of the end of Hubble. They are two completely different telescopes in two different places. Certainly the JWST is much more powerful and revolutionary, but that is not why it replaces its predecessor.
In addition, Hubble has received funding from NASA to operate until the year 2026, as long as it is in perfect condition to continue operating.
The JWST has a minimum mission duration of five years. However, like Hubble, it is expected to function well beyond its original lifespan. Its main limiting factor is fuel. NASA predicts up to 10 years of full operation without major problems, so there is still a lot to see.
[ad_2]